c++ program to read shapefile header. Shapefile can be read if you know the format of Shapefile files i.e of .shp, .shx, and .dbf file. ESRI provided technical description of the Shapefile files which describes very clearly about the format of storage of data in all three formats i.e .shp, .shx and .dbf. You can also interpret and take the advantage to make simple GIS tool which can read and edit Shapefile properly. Here is the link of the Shapefile technical descrption :
ESRI Technical Discription. This program reads only Shapefile .shp header, which includes file code, length, version, bounding box coordinates and the type of shape Shapefile you loaded. You can also find simple program that just reads about bounding box of that shapefile. The code is explained with the comments provided in all function that you found.
c++ program to read shapefile header:
#include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; class ByteConverter { public: //Convert 32 bits which is stored in BigEndian format to integer. This is performed with the help of bit operation i.e left shifting and operating or. static int32_t bigEndianIntRead(char *fileBuf, int startIndex) { return (((fileBuf[startIndex + 0] & 0xff) << 24) | ((fileBuf[ + 1] & 0xff) << 16)| ((fileBuf[startIndex + 2] & 0xff) << 8) | ((fileBuf[startIndex + 3] & 0xff))); } //Convert 32 bits which is stored in BigEndian format to integer. This is performed with the help of bit operation i.e left shifting and operating or. static int32_t littleEndianIntRead(char *fileBuf, int startIndex) { return (((fileBuf[startIndex + 3] & 0xff) << 24) | ((fileBuf[startIndex + 2] & 0xff) << 16) | ((fileBuf[startIndex + 1] & 0xff) << 8) | ((fileBuf[startIndex + 0] & 0xff))); } //Convert 64 bits or 8 Byte which is stored in BigEndian format to integer. This is performed with the help of bit operation i.e left shifting and operating or. static double littleEndianDoubleRead(char *fileBuf,int startIndex) { double convert; char *add; int j; add = new char(); j=-1; for(int i=startIndex; i<startIndex+8; i++) { j++; add[j] = fileBuf[i]; } convert = *reinterpret_cast<double * const>(add); return convert; } }; //Class HeaderShapefile have all funtion implemented to desribe every field of shapefile header file. class HeaderShapefile { public: //filecode describes the code of .shp file. As described in Shapefile Technical description of ESRI, filecode //value is always constant and should have 9994 value. static int32_t fileCode(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::bigEndianIntRead(fileBuf,startIndex); } //File length contains Length of the file field static int32_t fileLength(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::bigEndianIntRead(fileBuf,startIndex); } //Version function static int32_t version(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianIntRead(fileBuf,startIndex); } //Function shapeType describes the type of the shape. It returns an 32 bit integer //value. This integer is then matched with the cooresponding shape as described in ESRI shapefile pdf static int32_t shapeType(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianIntRead(fileBuf,startIndex); } //This remaning funtion of the class will calculate the bounding box coordinates of the shapefile. //Following values i.e x and y minimum and maximum values also with z and m minimum // and maximum values are obtained. static double dimensionXMin(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf,startIndex); } static double dimensionYmin(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } static double dimensionXmax(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } static double dimensionYmax(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } static double dimensionZmin(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } static double dimensionZmax(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } static double dimensionMmin(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } static double dimensionMmax(char*fileBuf, int startIndex) { return ByteConverter::littleEndianDoubleRead(fileBuf, startIndex); } }; class SizeOfFile { public: //This function finds the size of file in Byte static long sizeOfFiles(FILE *file) { long l, e; l = ftell(file); fseek(file, 0, 2); e = ftell(file); fseek(file, l, 0); return e; } }; int main() { int32_t filecodes, fileLengths, shapeTypes, versions; double xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, mmin, mmax, zmin, zmax; string shape; char *filePath = "map.shp"; char*fileBuf; // Pointer to our buffered data FILE *file = NULL; // File pointer // Open the file in binary mode using the "rb" format string // This also checks if the file exists and/or can be opened for reading correctly if ((file = fopen(filePath, "rb")) == NULL) cout << "Could not open specified file" << endl; else cout << "File opened successfully" << endl; // Get the size of the file in bytes long fileSize = SizeOfFile::sizeOfFiles(file); // Allocate space in the buffer for the whole file fileBuf = new char[fileSize]; // Read the file in to the buffer fread(fileBuf, fileSize, 1, file); // Now that we have the entire file buffered, we can take a look at some binary infomation cout<<"File size = " <<fileSize; cout<<"File size get = "<<fileBuf; filecodes = HeaderShapefile::fileCode(fileBuf,0); fileLengths = HeaderShapefile::fileLength(fileBuf,24); versions = HeaderShapefile::version(fileBuf,28); shapeTypes = HeaderShapefile::shapeType(fileBuf,32); xmin = HeaderShapefile::dimensionXMin(fileBuf,36); ymin = HeaderShapefile::dimensionYmin(fileBuf,44); xmax = HeaderShapefile::dimensionXmax(fileBuf,52); ymax = HeaderShapefile::dimensionYmax(fileBuf,60); zmin = HeaderShapefile::dimensionZmin(fileBuf,68); zmax = HeaderShapefile::dimensionZmax(fileBuf,76); mmin = HeaderShapefile::dimensionMmin(fileBuf,84); mmax = HeaderShapefile::dimensionMmax(fileBuf,92); /*****************HEADER SHAPEFILE DETAIL*********************/ cout<<endl<<"/*****************HEADER SHAPEFILE DETAIL*********************/"; cout<<endl<<"File code = "<<filecodes<<endl; cout<<"File Length = "<<fileLengths<<endl; cout<<"Version = "<<versions<<endl; //This shapefile shapetypes can be found in the technical discription. switch(shapeTypes) { case 0: shape = "Null Shape"; break; case 1: shape = "Point"; break; case 3: shape = "Poly Line"; break; case 5: shape = "Polygon"; break; case 8: shape = "MultiPoint"; break; case 11: shape = "PointZ"; break; case 13: shape = "PolyLineZ"; break; case 15: shape = "PolygonZ"; break; case 18: shape = "MultiPointZ"; break; case 21: shape = "PointM"; break; case 23: shape = "PolyLineM"; break; case 25: shape = "PolygonM"; break; case 28: shape = "MultiPointM"; break; case 31: shape = "MultiPatch"; break; default: shape = "Wrong match found"; break; } cout<<"Shape Type = "<<shape<<endl; cout<<endl<<"************* Bounding Box **************"<<endl; cout<<"X minimum = "<<xmin<<endl; cout<<"Y minimum = "<<ymin<<endl; cout<<"X maximum = "<<xmax<<endl; cout<<"Y maximum = "<<ymax<<endl; cout<<"Z minimum = "<<zmin<<endl; cout<<"Z maximum = "<<zmax<<endl; cout<<"M minimum = "<<mmin<<endl; cout<<"M maximum = "<<mmax<<endl; cin.get(); delete[]fileBuf; fclose(file); // Almost forgot this return 0; }
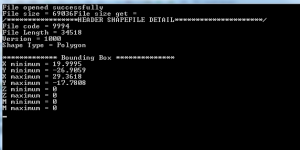
Output of c++ program to read shapefile header: