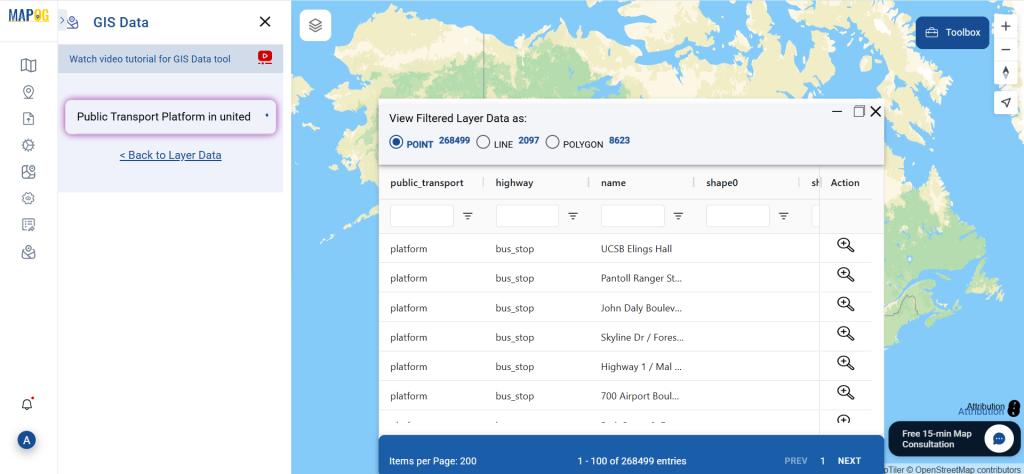
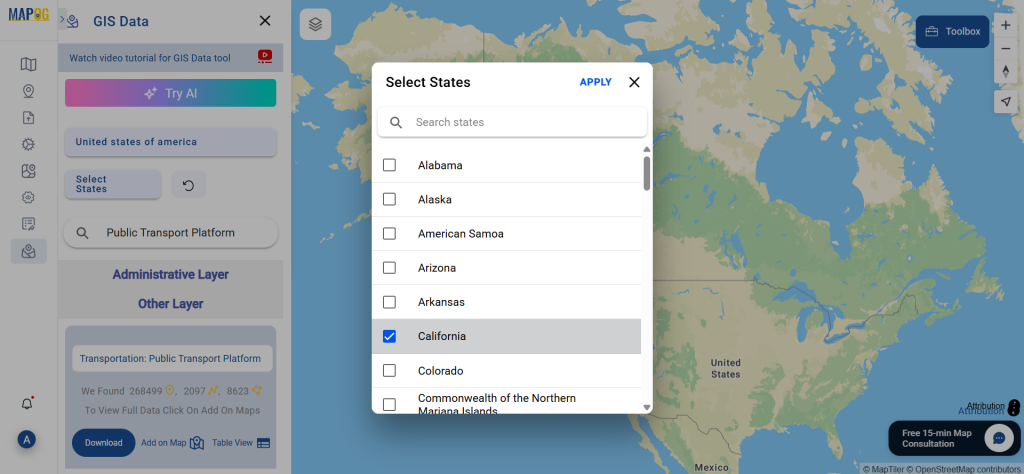
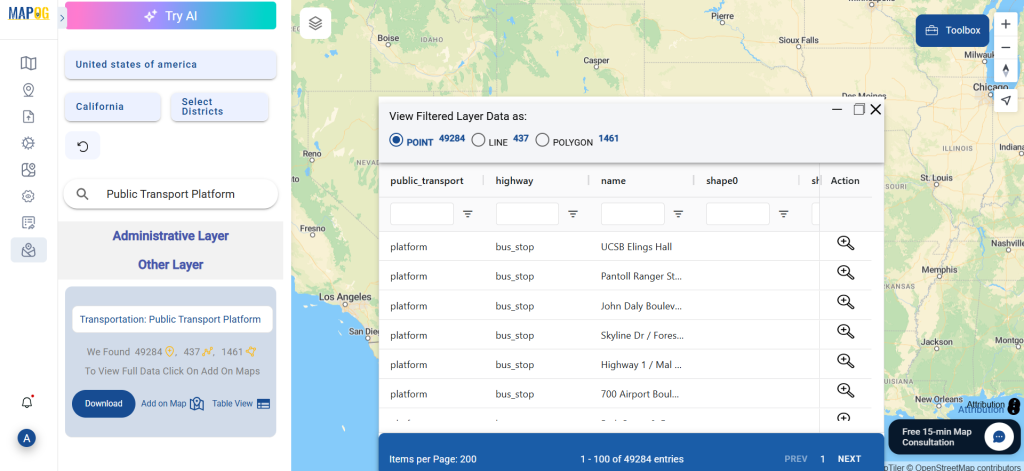
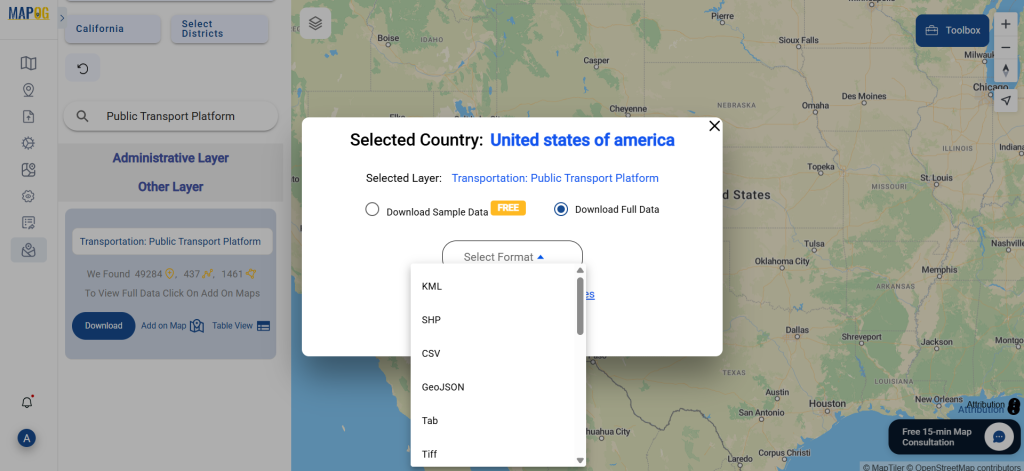
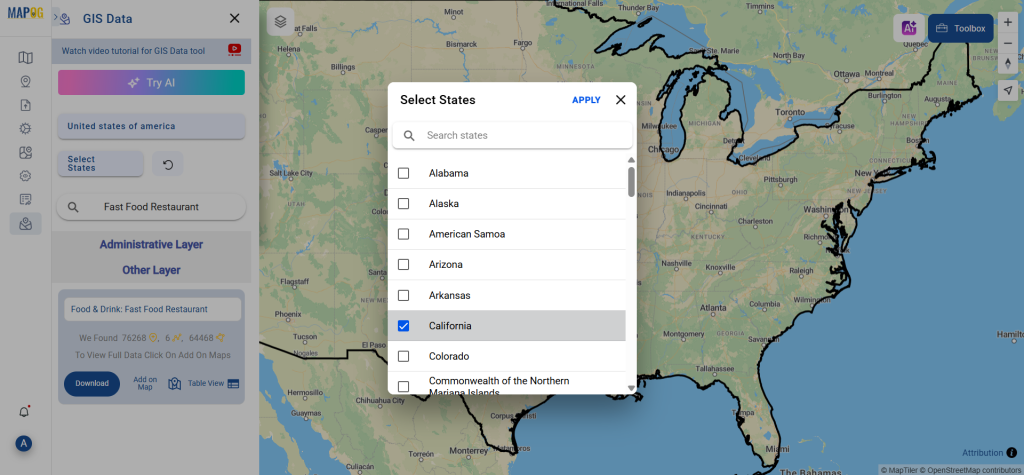
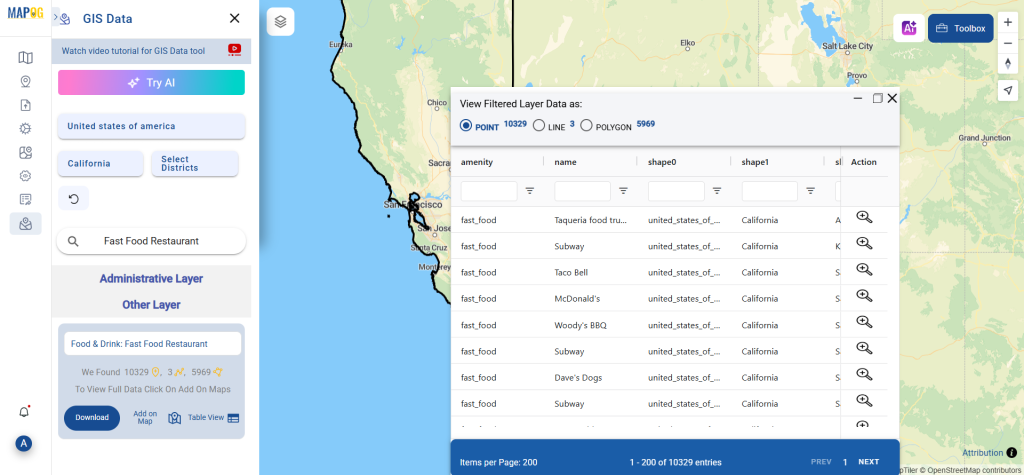
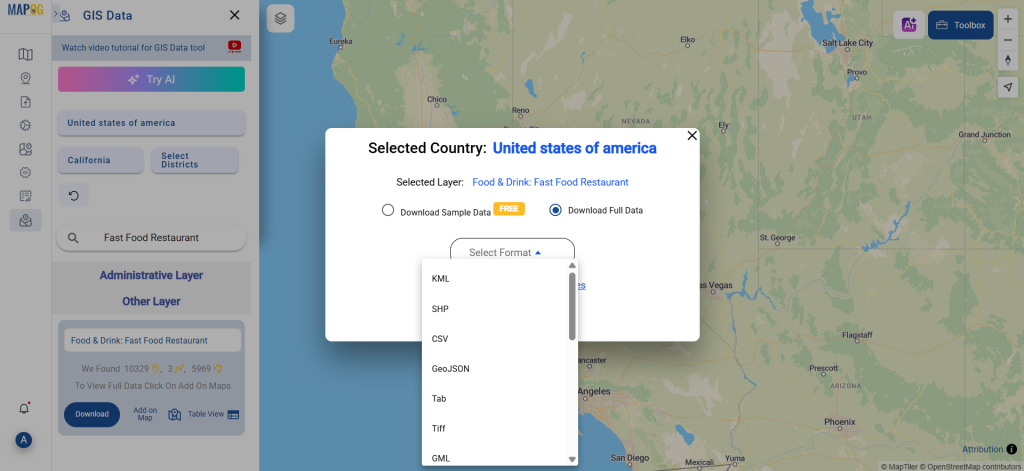
A crucial part of the GIS process involves file conversion, which ensures that information flows smoothly across different platforms. To make this process effortless, the MAPOG Converter Tool comes into play—it allows users to quickly and efficiently convert data between multiple formats.
What is SHP File?
In GIS, one of the most commonly used geographic vector data formats is the SHP file (Shapefile). It stores both the attribute data, which describes the features, and the geometry, which includes points, lines, and polygons. Additionally, SHP files work seamlessly with applications like ArcGIS and QGIS, making them ideal for mapping locations, boundaries, and other spatial data. Moreover, these files often come with additional supporting files that store related information.
Online GIS Data Conversion
Key Concept for Conversion SHP to KMZ:
To make the conversion process even smoother, MAPOG’s Converter Tool provides a simple and intuitive platform. With its user-friendly interface, users can move through each step without any hassle. Whether you want to convert SHP to KMZ or any other format, MAPOG ensures that the process is both fast and accurate.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting SHP to KMZ
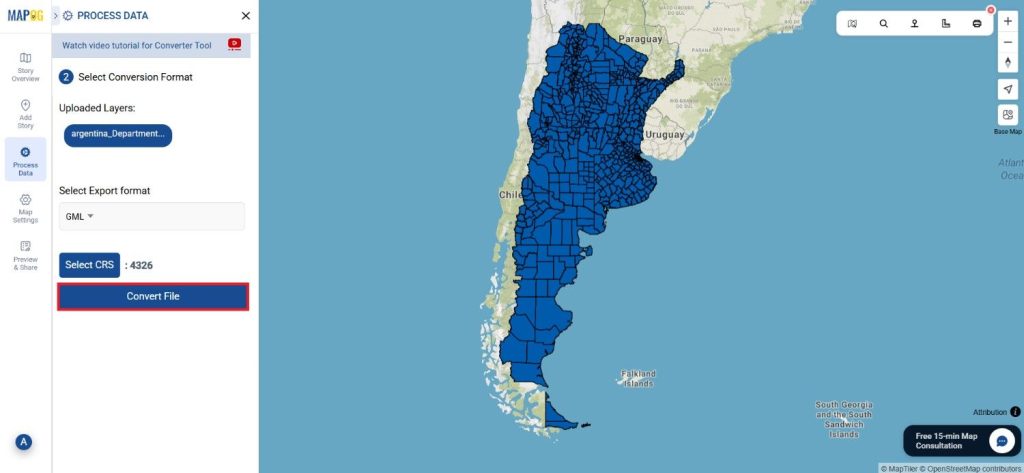
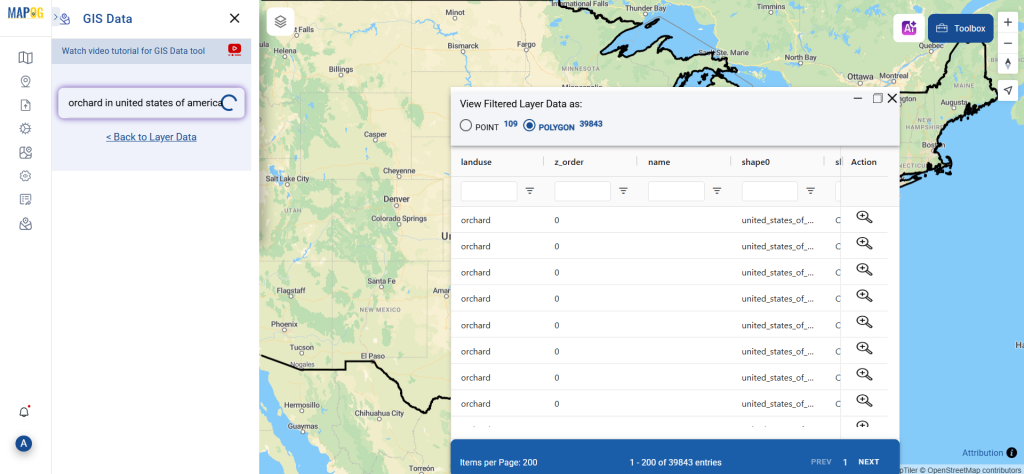
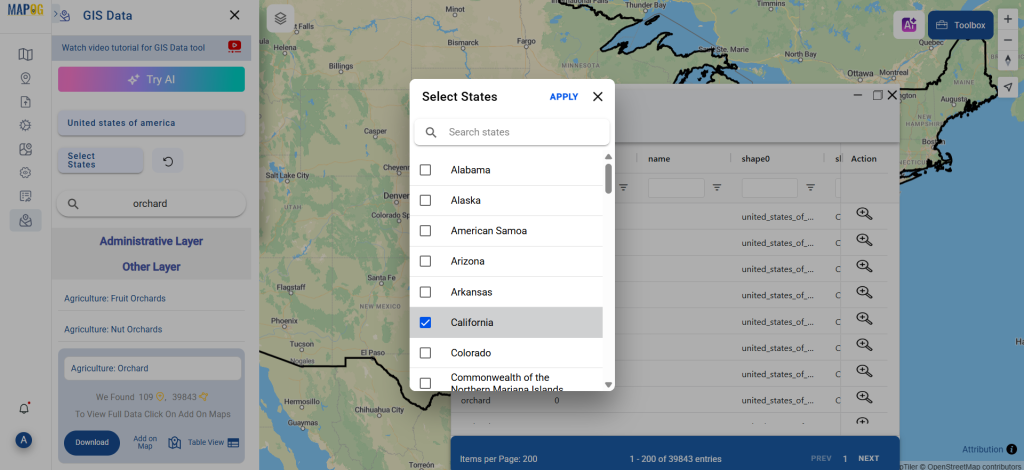
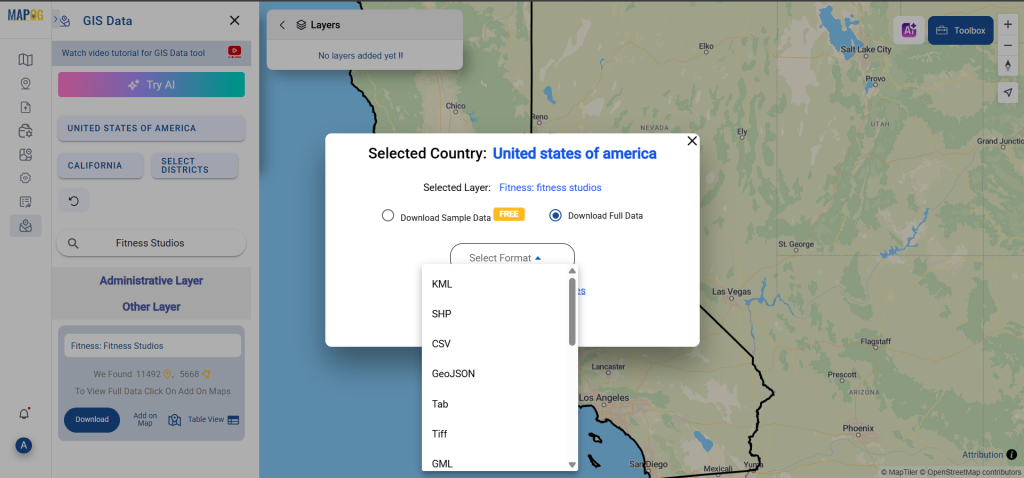
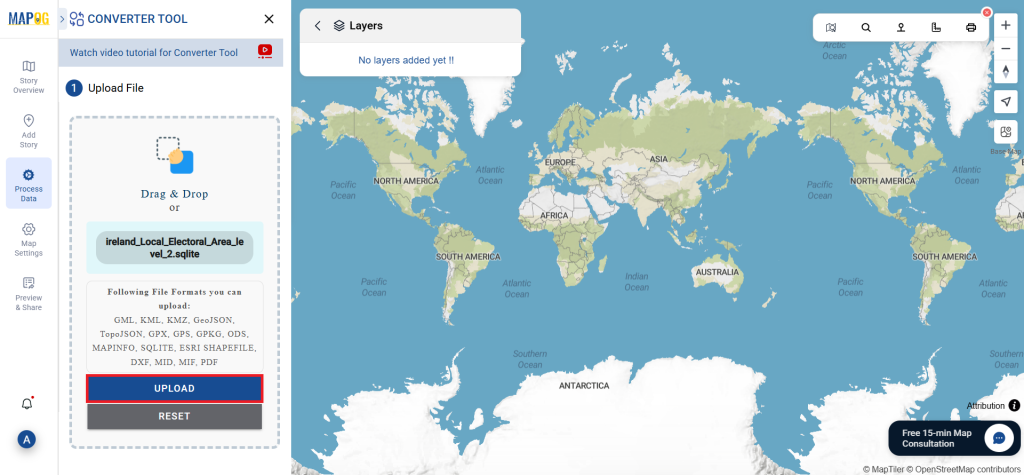
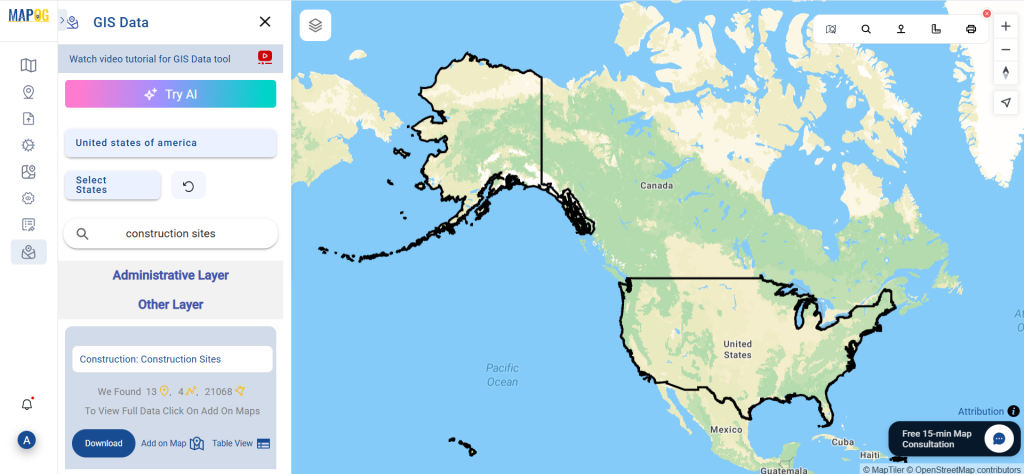
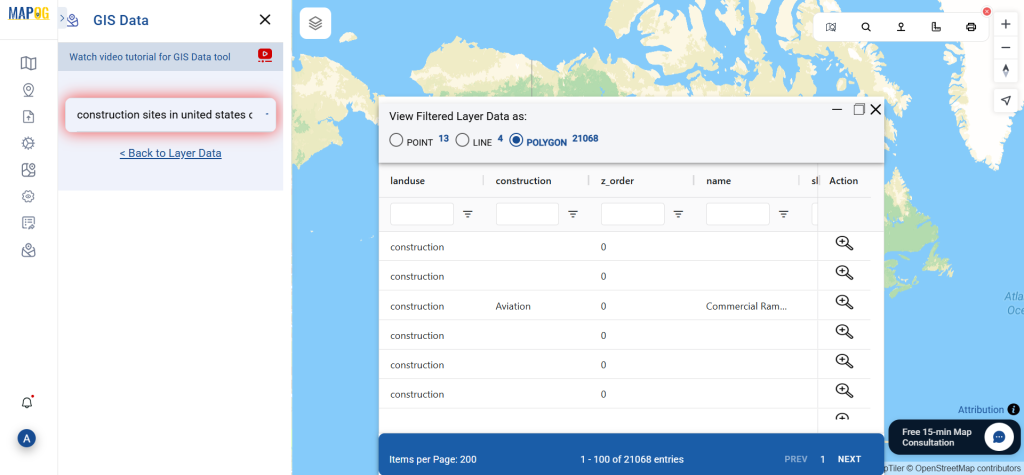
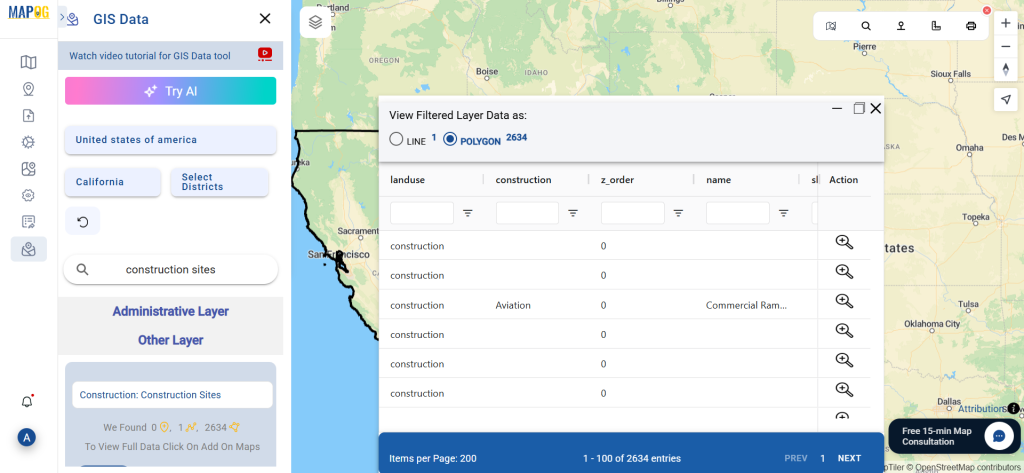
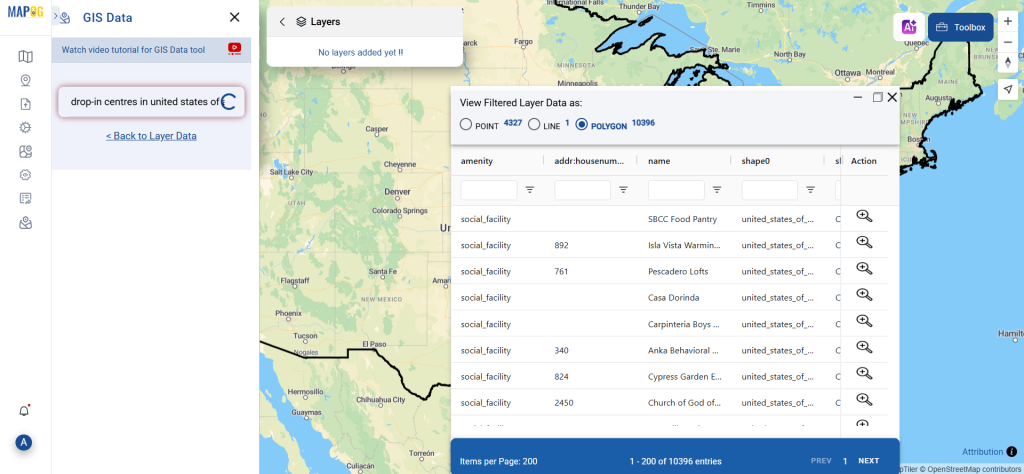
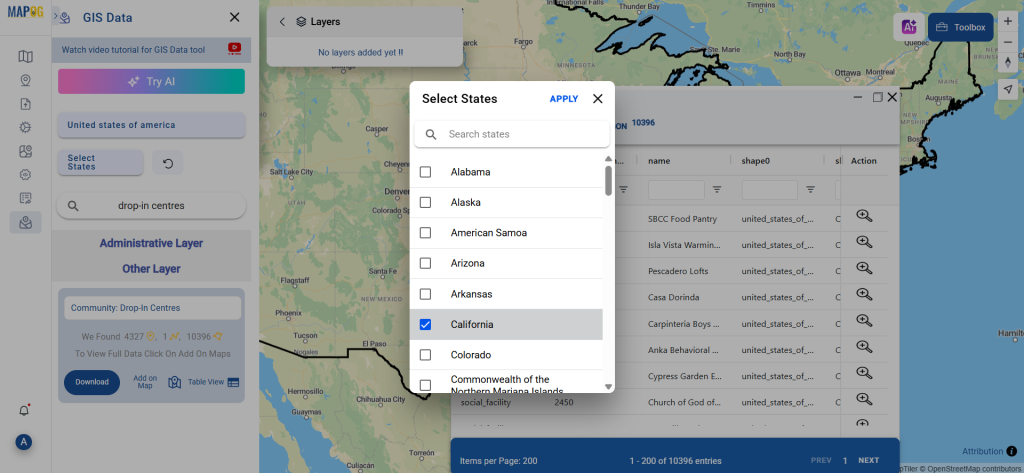
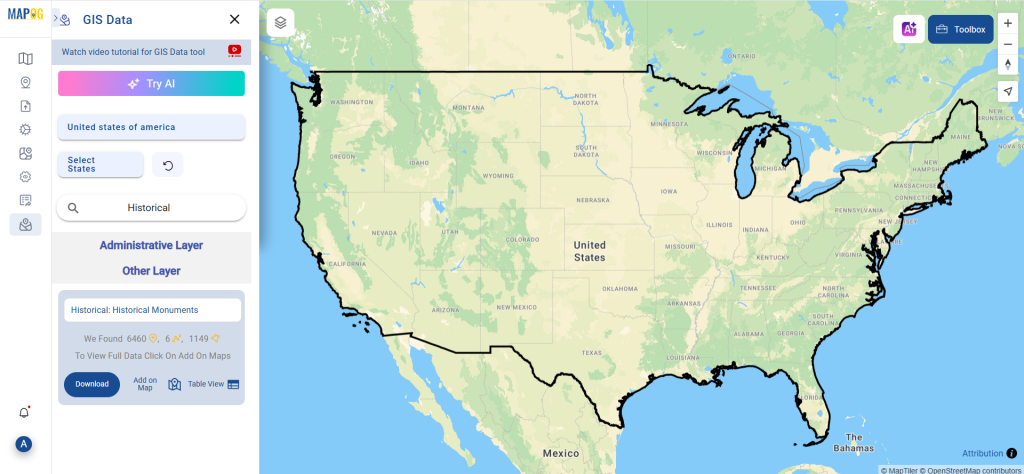
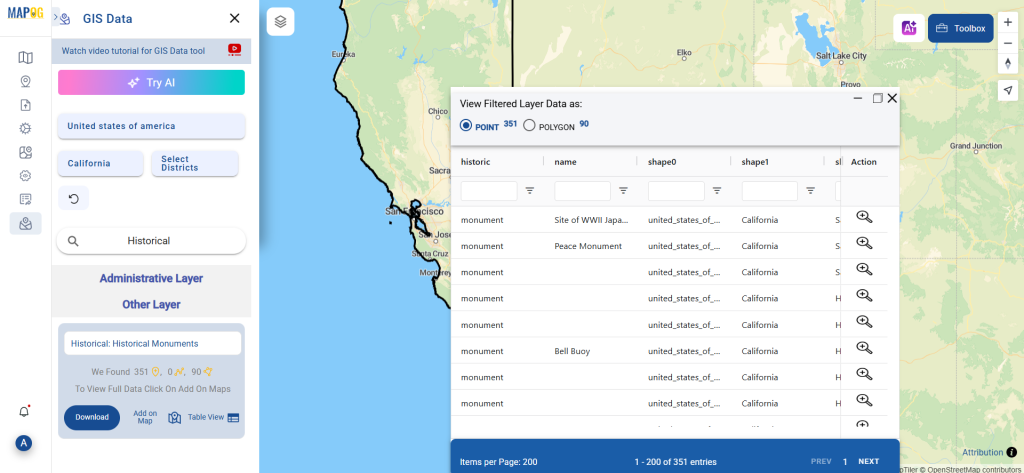
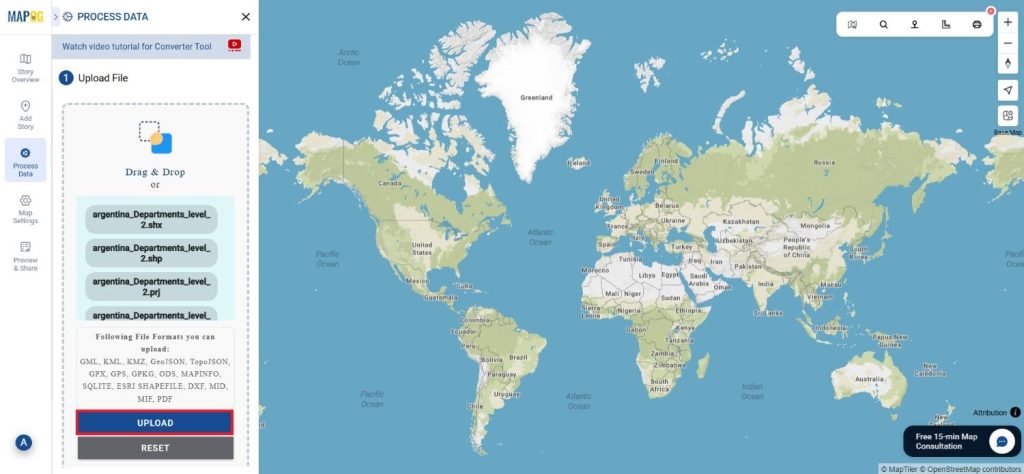
Step 1: Upload the Data
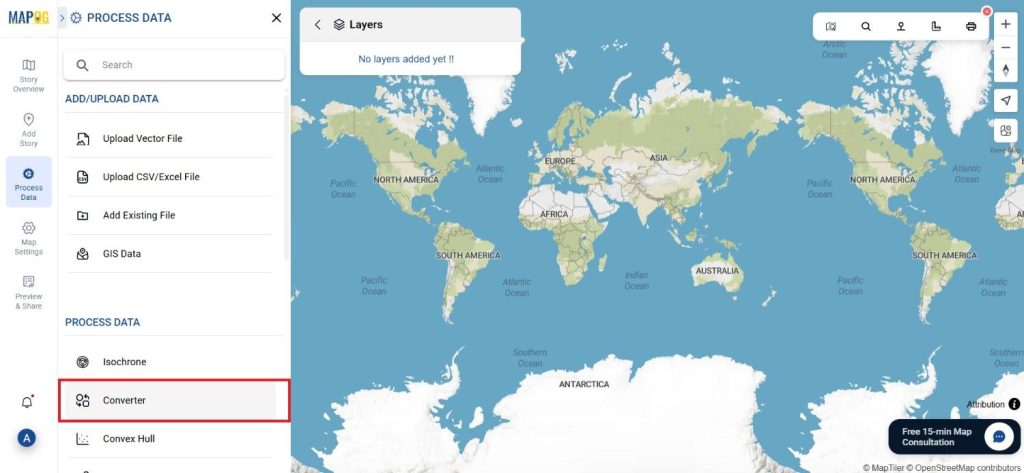
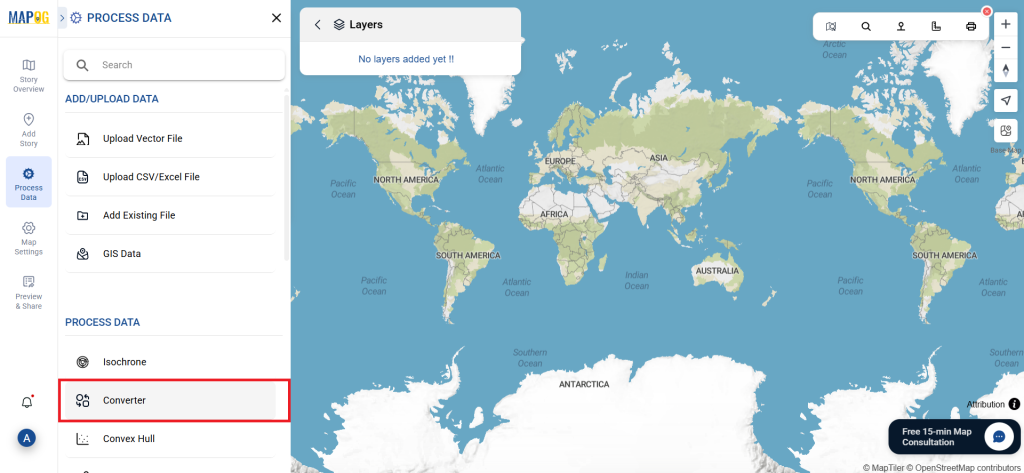
Start by selecting the “Process Data” section in MAPOG Map Analysis. From there, choose the “Converter Tool” option.
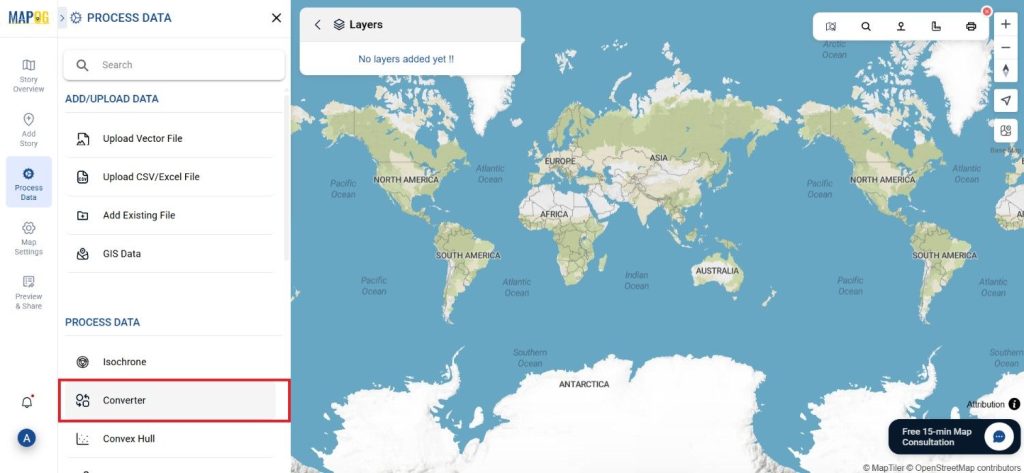
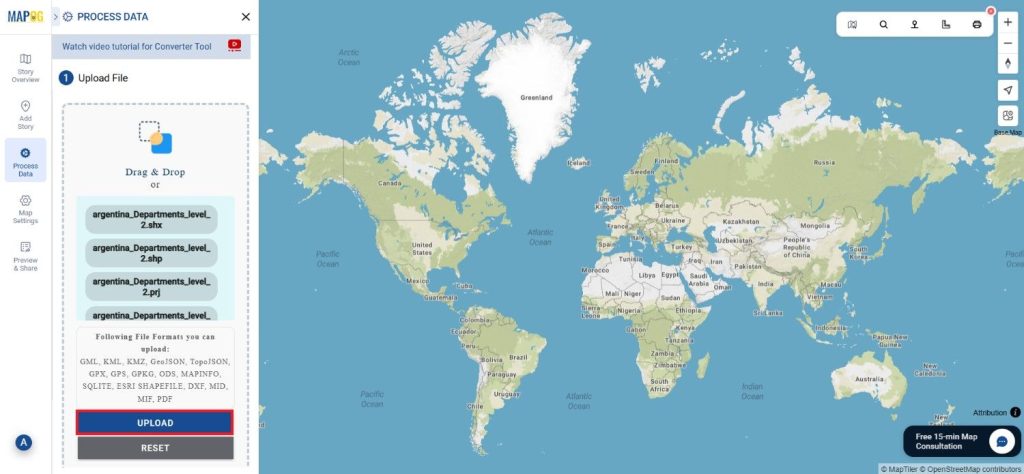
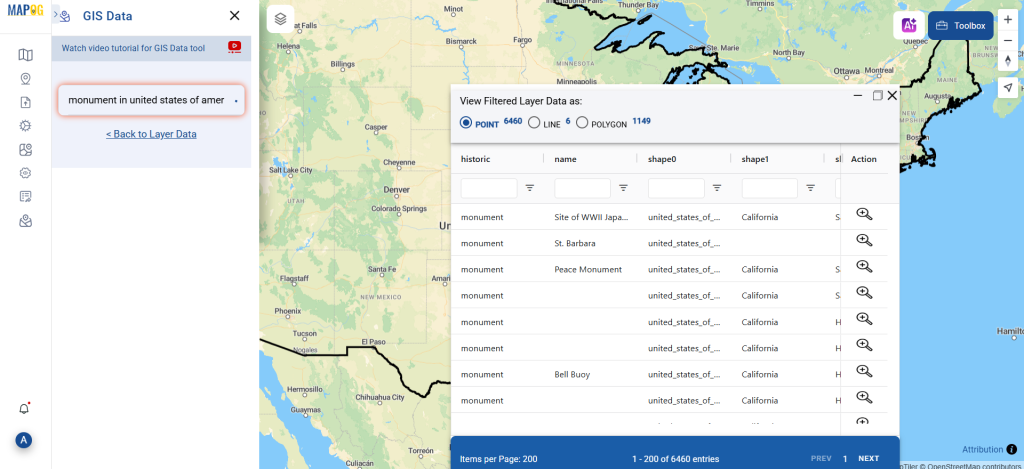
Before uploading your SHP file, make sure it is ready for conversion.
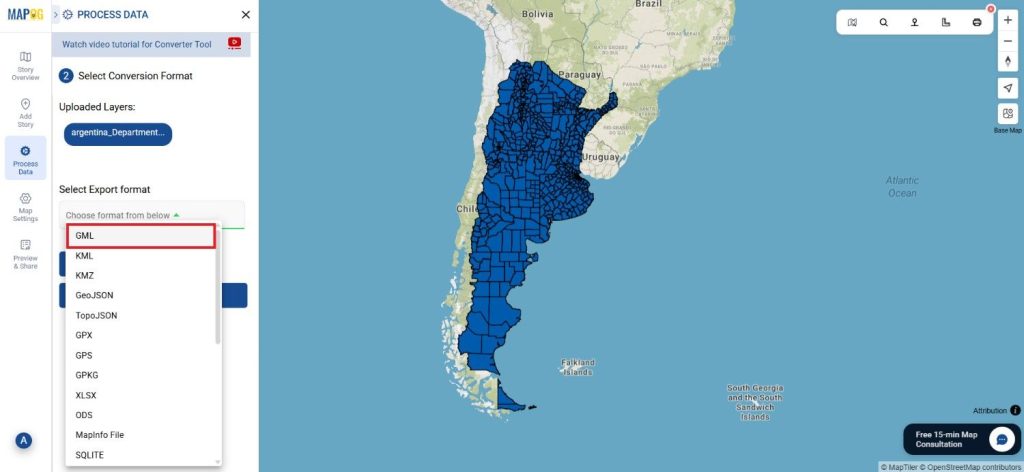
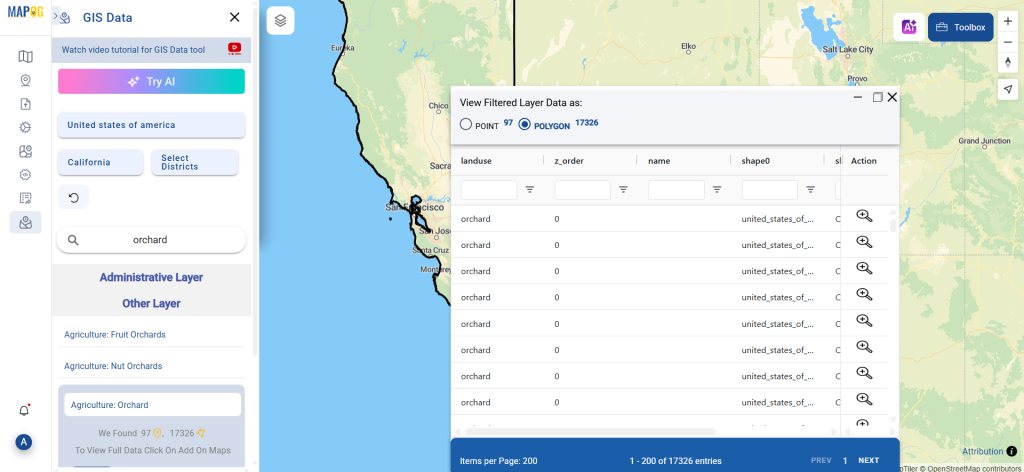
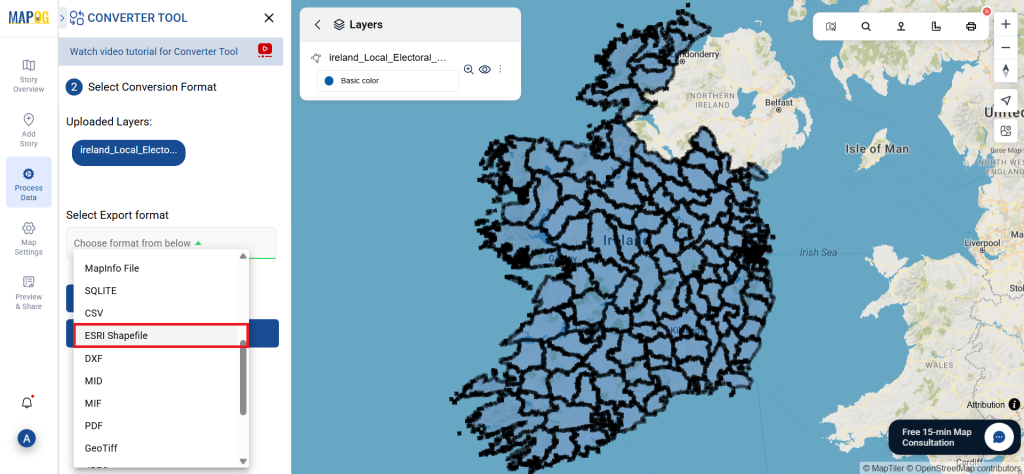
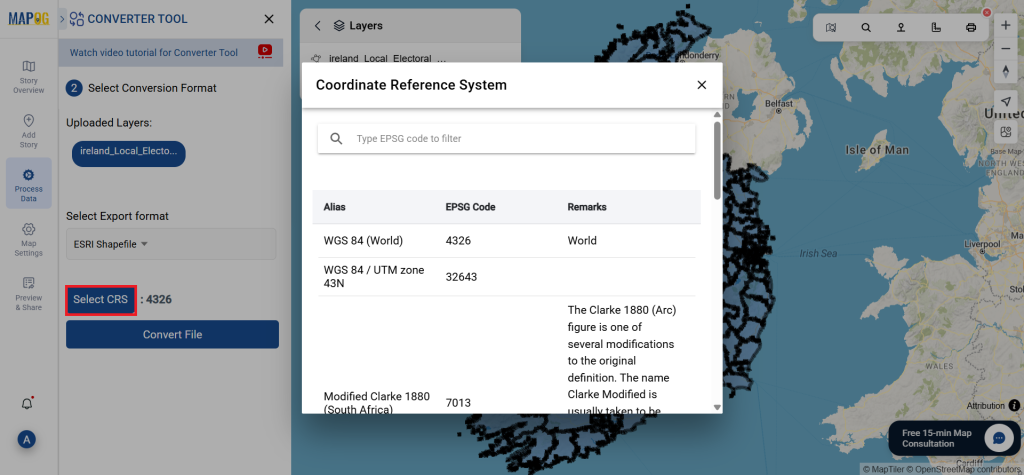
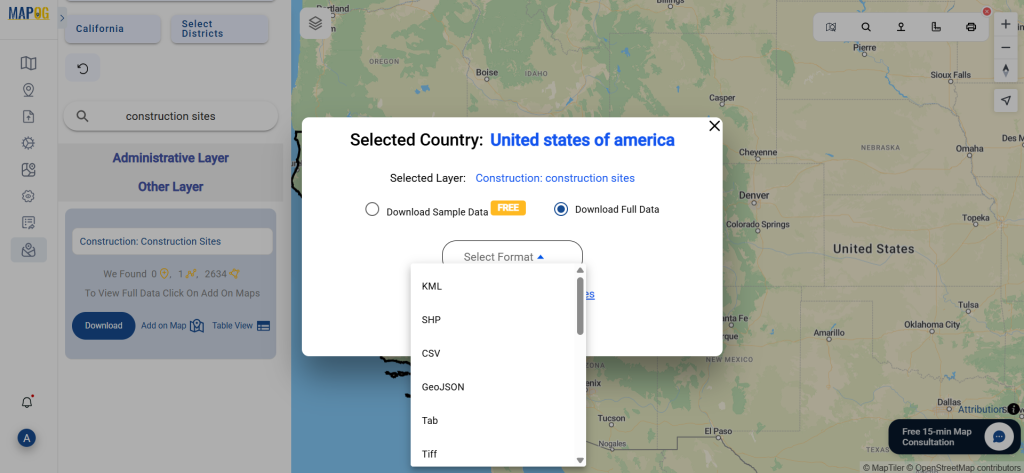
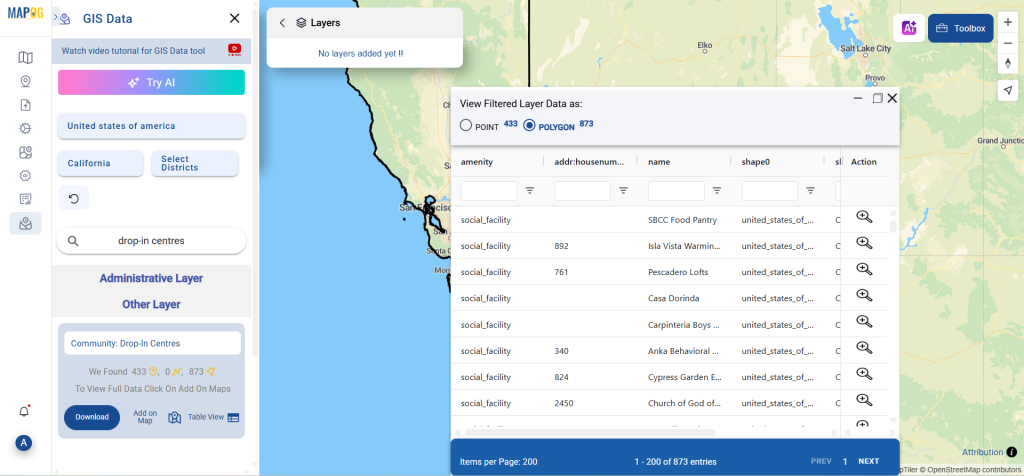
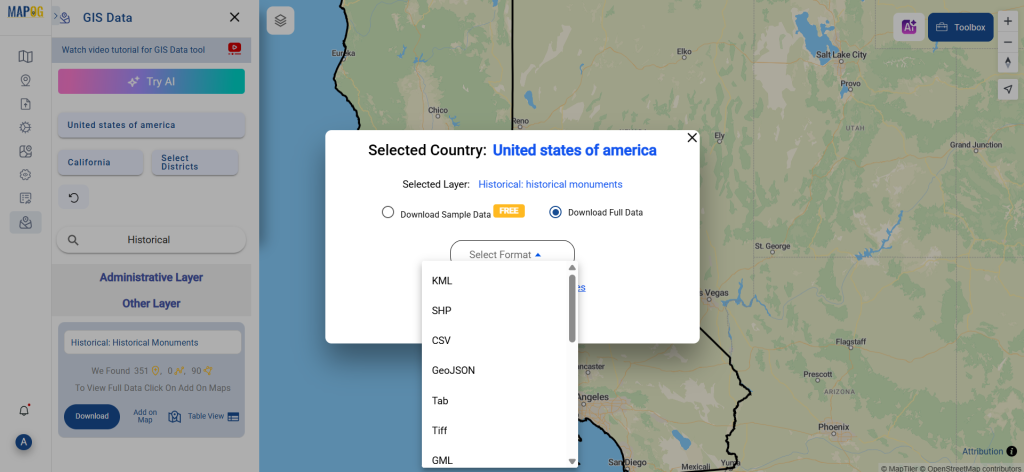
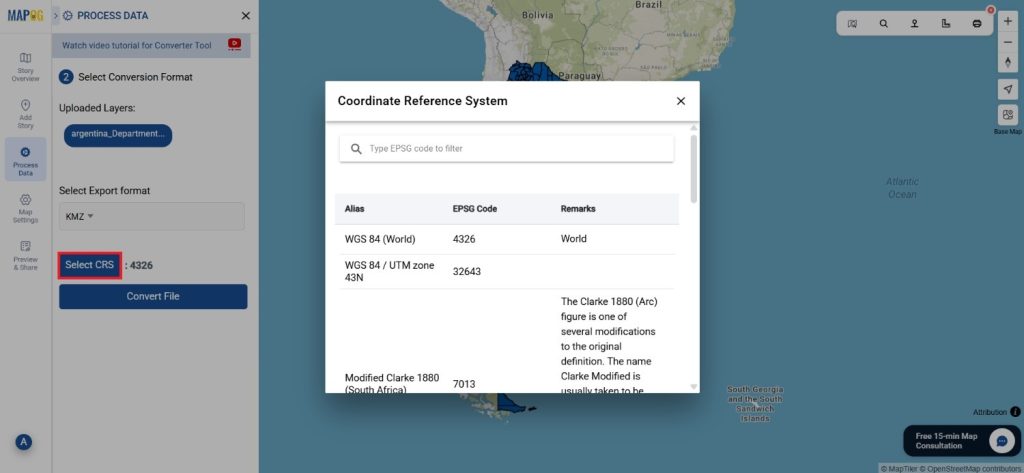
Step 2: Select the Format for Conversion
Next, select KMZ as the output format. KMZ is widely used for displaying geographic data in Google Earth and other web-based mapping platforms, making it a versatile format for visualization and sharing.

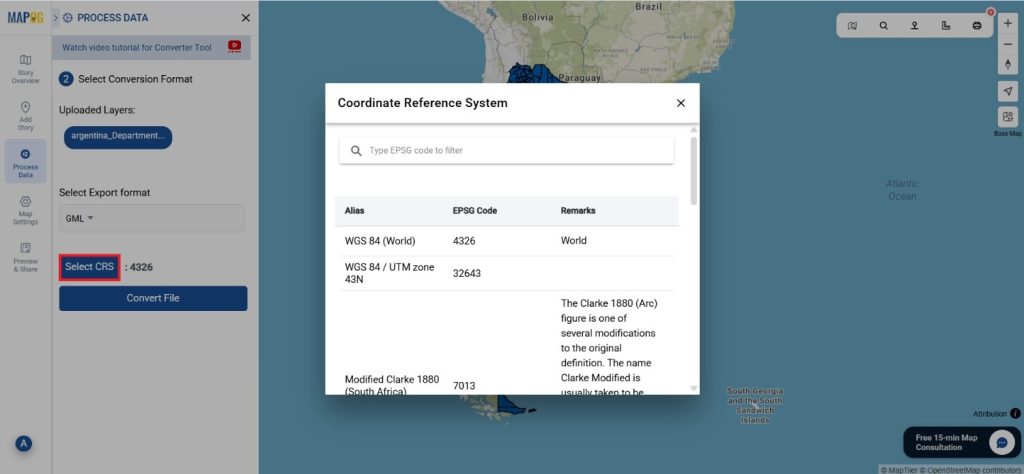
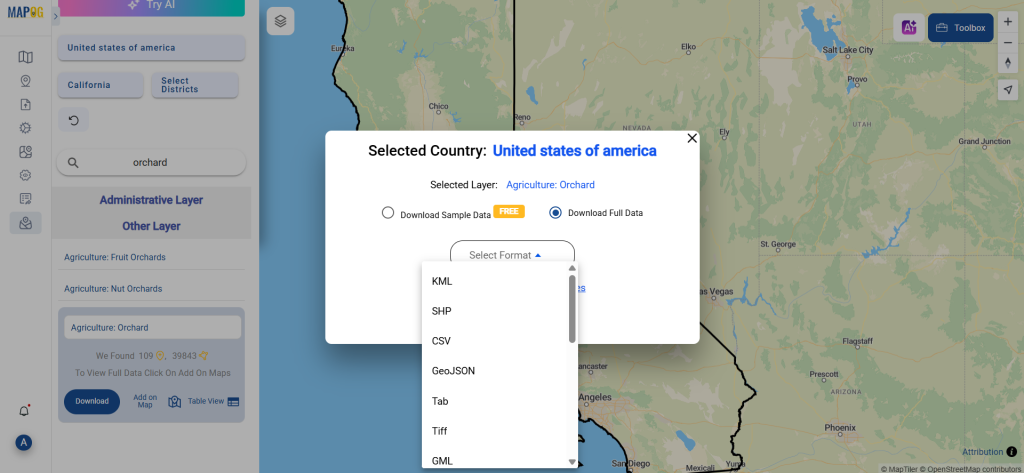
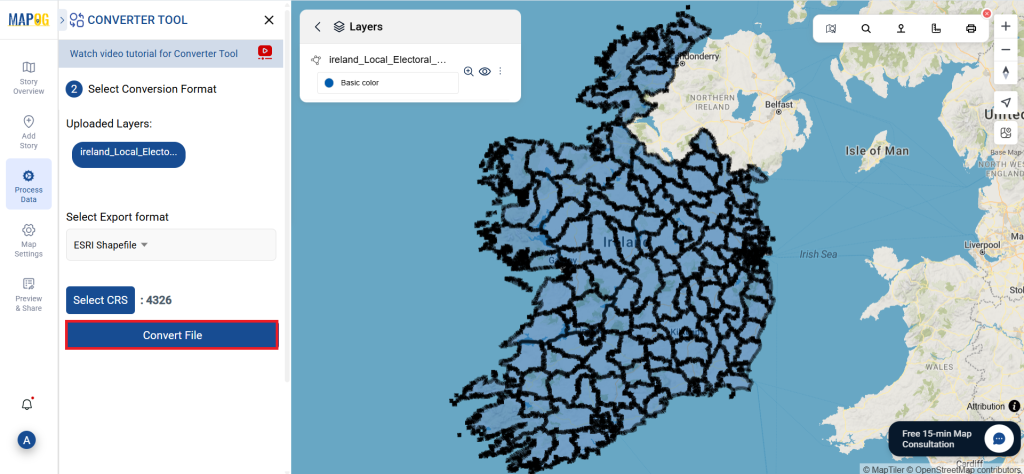
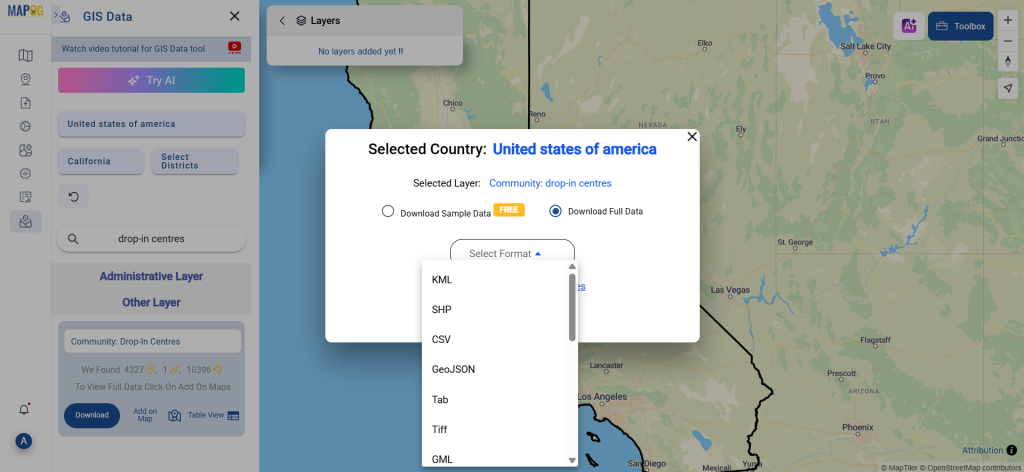
Step 3: Execute the Conversion
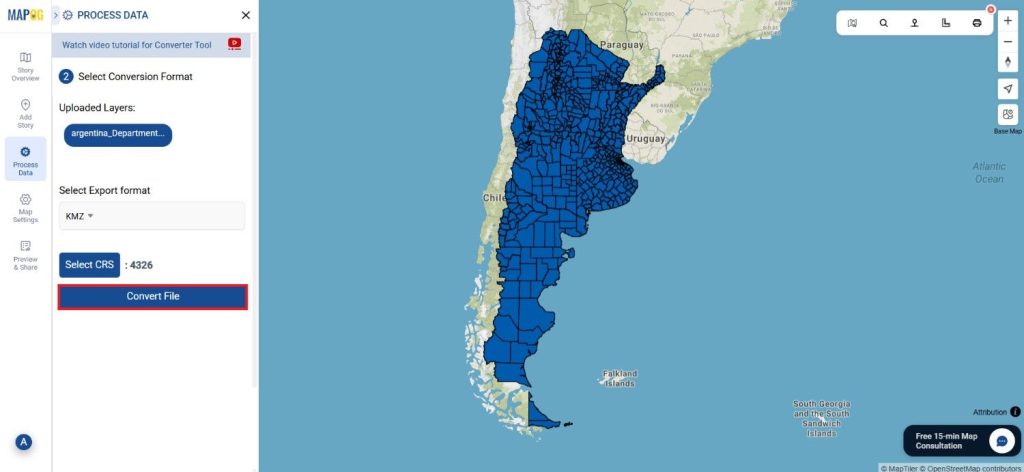
Once you’ve chosen the KMZ format and set the CRS, proceed with the conversion process.
The MAPOG tool will efficiently convert your SHP file into KMZ format, allowing for easy integration into Google Earth and similar tools.
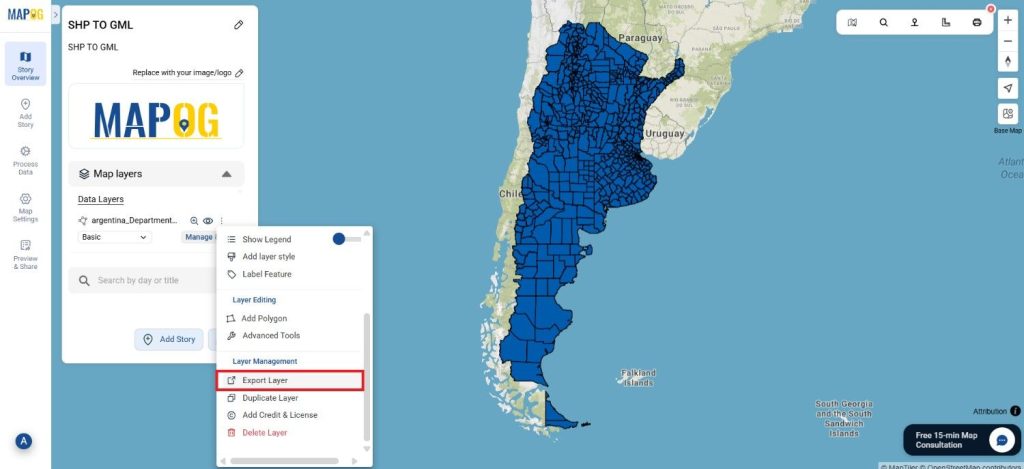
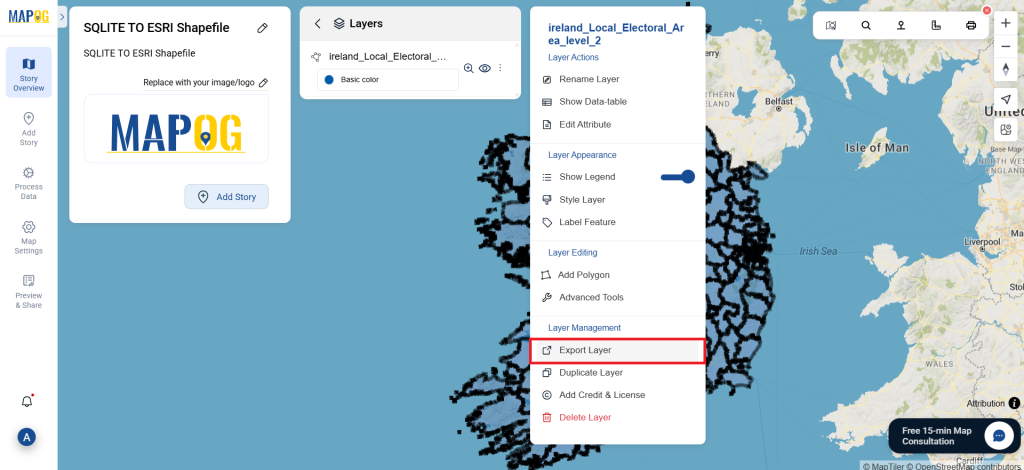
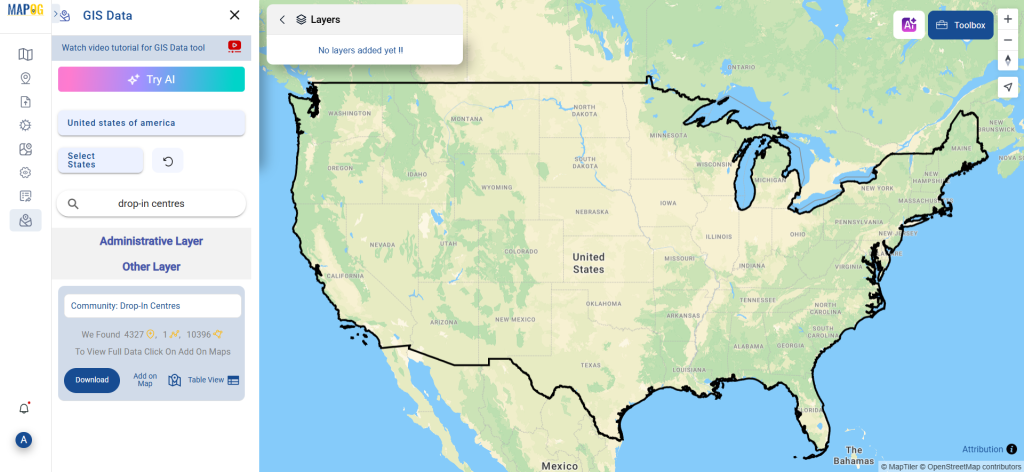
Step 4: Review and Download
After the conversion is complete, review the output to ensure the data was accurately converted. Finally, download the KMZ file.

Conclusion:
The MAPOG Converter Tool simplifies the process of converting data between different formats, making it an essential resource for GIS professionals. By following these simple steps, you can easily convert SHP files to KMZ format, ensuring your data is ready for use in web mapping applications and interactive visualizations.
Additional Tools for Further Analysis:
With MAPOG’s versatile toolkit, you can effortlessly upload vectors and upload Excel or CSV data, incorporate existing layers, perform polygon splitting, use the converter for various formats, calculate isochrones, and utilize the Export Tool.
Learn About MAPOG:
MAPOG is perfect for people who want to use visually striking and interactive maps to make their data come to life. It lets you build engaging narratives by connecting maps with visuals like text and images. Producing shareable content is made easy with MAPOG, whether you’re marketing a project, giving a tour or presenting research.
Here are some other blogs you might be interested in:
- Convert Online GIS data : KML to PDF file
- Converting KML to GeoTIFF , Online Gis Data Converter
- Converting KMZ to SHP : Online GIS Data Conversion
- Converting TopoJSON to SHP Online : GIS Data Converter
- Converting GeoJSON to TopoJSON with MAPOG
- Converting GeoJSON to CSV with MAPOG
- Converting KMZ to KML with MAPOG
- Converting GML to KML with MAPOG
- Convert KMZ to TopoJSON Online
- Converting KMZ to GeoJSON Online
- Convert KML to MID Online
- Online Conversion KML to MIF